Many people who experience stomach pain or indigestion assume it is just biliary stones or gallstone cholelithiasis. However, because the symptoms are so similar, it is common to wonder, “can gallstones cause cancer?” While the two conditions are different, this overlap creates confusion and often delays a proper diagnosis. This is why questions like can gall bladder stones cause cancer are frequently asked by patients seeking clarity.
Understanding the distinction between Gallbladder Cancer vs Gallstones is vital for early intervention and effective treatment. So, how do you tell the difference? Let’s break it down in simple words with insights from Dr. MSS Keerthi, a Gallbladder Cancer Specialist in Hyderabad with over 17 years of experience in treating complex gallbladder and gastrointestinal cancers.
In This Blog, You Will Learn:
- How gallstones and gallbladder cancer differ
- Why their symptoms often cause confusion
- Key warning signs that may point to cancer
- Diagnosis and treatment options for both conditions
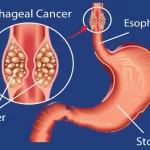
What Are Gallstone Cholelithiasis?
Gallstones are small, hardened deposits that form inside the gallbladder, a condition medically known as cholelithiasis. These calculi are usually made of cholesterol, bile salts, or waste products. In most cases, gallstones cause abdominal pain, bloating, or nausea, especially after eating fatty meals. They can be present in different sizes such as gallstones 1 cm, 6mm & 9 mm, and symptoms often depend on their size and position within the gallbladder.
What Is Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious disease where abnormal cells grow in the lining of the gallbladder. Unlike gallstones, it often does not show clear symptoms until it is advanced, making it more dangerous if ignored, especially in some cases where a large gallstone may be present alongside the disease.
Similarities in Cholelithiasis Symptoms:
The main reason people mix up gallbladder cancer vs gallstones is that both can cause:
- Pain in the upper right abdomen
- Nausea or vomiting
- Indigestion or bloating
- Jaundice (yellowing of eyes or skin in some cases)
Because of these shared signs, patients may think it’s just gallstones when it could be something more serious. This confusion often delays diagnosis, especially when people are unaware of the gall bladder stones reason, the common stones in gallbladder causes, or the fact that long-standing stones raise concerns about whether gall bladder stone cause cancer in certain high-risk cases.
Can Gallstones Lead to Gallbladder Cancer?
Yes, in some cases, gallstones can increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Long-standing gallstones cause repeated irritation and inflammation of the gallbladder wall. Over time, this chronic irritation may lead to abnormal cell changes. Research shows that the large gallstone risk of cancer is higher, especially when stones are present for many years without treatment. This is why many people ask, can gallbladder stones turn into cancer—the answer is that the risk exists, but it is not the same for everyone.
How gallstones may increase cancer risk:
- Chronic inflammation: Continuous irritation from stones damages the gallbladder lining.
- Large or multiple stones: Bigger stones or long-term cholelithiasis causes more stress on the gallbladder wall.
- Long duration: Gallstones present for 10–20 years carry a higher risk than recently formed stones.
- Repeated infections: Frequent gallbladder infections increase cellular damage.
- Calcified gallbladder: Long-standing stones can lead to a “porcelain gallbladder,” which is linked to cancer risk.
It is important to remember that not everyone with gallstones develops gallbladder cancer. Many people with cholelithiasis never face serious complications. However, persistent symptoms, large stones, or long-term gallstones should never be ignored. Early medical evaluation and timely treatment can significantly reduce future risks.
Differences Between Gallbladder Cancer And Gallstones:
While gallstones and gallbladder cancer may look similar, some warning signs lean more toward cancer:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Constant dull pain that does not go away
- Swelling or a lump in the abdomen
These are less common with simple gallbladder disease than with cancer.
When to Suspect Gallbladder Cancer:
If you have long-standing gallstones with sudden changes in symptoms, or if your doctor finds thickening of the gallbladder wall during tests, cancer may be suspected. Knowing how to know if a gallstone is cancer is not possible by symptoms alone—it needs proper medical evaluation, especially because many patients worry whether a gall bladder stone cause cancer in such situations.
Tests to Tell the Difference Gallbladder Cancer And Gallstones:
To clearly difference between gallstones and gallbladder cancer, doctors may suggest:
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
- CT or MRI scan
- Blood tests for liver function
- Biopsy in suspected cases
These investigations help in confirming whether it’s gallbladder cancer vs gallstones.
All these diagnostic tests are available at Hills Gastro & Onco Care, ensuring patients receive accurate evaluation under one roof. With the guidance of Dr. M.S.S. Keerthi, an experienced cancer specialist, results are carefully interpreted to arrive at the right diagnosis and plan timely, appropriate treatment without delay.
Treatment Implications - Gallstones vs Cancer:
- Gallstones: Usually treated by surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). It is a common and safe procedure.
- Gallbladder Cancer: Requires more advanced treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation. Early detection improves the chances of successful treatment.
Prevention & Risk Reduction:
While gallstones cannot always be prevented, lifestyle choices can reduce risks:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a balanced diet, avoid excess fried foods.
- Manage diabetes and cholesterol.
- Do regular health check-ups if you have a family history?
Conclusion:
Gallstones are common and usually harmless if treated on time. But gallbladder cancer, though rare, can be life-threatening if missed. Because the symptoms of gallbladder cancer and gallstones often overlap, it is important not to ignore persistent abdominal issues. If you notice unexplained weight loss, continuous pain, or jaundice, consult a doctor immediately.
For expert guidance and accurate diagnosis, it’s best to consult Dr. M.S.S. Keerthi, the best cancer doctor in Hyderabad and an experienced Gallbladder Cancer Surgeon in Hyderabad. At Hills Gastro and Onco Care, Kompally, Dr. Keerthi and her team offer advanced diagnostic and surgical treatments, ensuring every patient receives the best possible care with compassion and precision. If you or a loved one are seeking specialized oncology care, you can book an appointment with Dr. MSS Keerthi to discuss a personalized treatment plan.
FAQs About Gallbladder Cancer vs Gallstones:
In some cases, small gallstones that do not cause symptoms may not need surgery. However, once gallstones start causing pain, infection, or blockages, surgery (cholecystectomy) is usually the best and most permanent solution. Medicines to dissolve gallstones are rarely effective and may not prevent them from coming back.
No, they are different. Gallstones are hard deposits formed from bile, while gallbladder polyps are small growths that develop on the inner wall of the gallbladder. Most polyps are harmless, but larger ones may increase the risk of cancer and should be monitored or removed by a specialist.
Yes, gallbladder cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease. It often goes unnoticed in the early stages because symptoms resemble those of gallstones or indigestion. Early diagnosis and treatment by an expert Gallbladder Cancer Surgeon in Hyderabad, like Dr. M.S.S. Keerthi at Hills Gastro and Onco Care, Kompally, can significantly improve outcomes.
While gallstones themselves do not directly cause cancer, having long-term gallstones can increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer. Chronic irritation and inflammation of the gallbladder lining due to stones can sometimes lead to precancerous changes. Regular check-ups and timely treatment are important to prevent complications.
Cholelithiasis is the medical term for gallstones. They are caused when your bile (digestive fluid) contains too much cholesterol or too much bilirubin. It can also happen if your gallbladder does not empty properly, causing the bile to become very concentrated and turn into stones.
“Calculi” is just another word for stones. If your ultrasound report says “multiple calculi,” it means you have several stones of various sizes inside your gallbladder. This condition usually requires a consultation with a specialist like Dr. MSS Keerthi to check for inflammation or blockage.
Think of it like sugar settling at the bottom of a cup of tea. When the chemicals in your bile (cholesterol and bile salts) are out of balance, they form tiny crystals. Over time, these crystals stick together and harden into solid stones.
It is not about the number, but the size and symptoms. A single large stone (over 3cm) can be more dangerous than ten tiny ones because large stones increase the risk of gallbladder cancer. Even one small stone is “too many” if it blocks your bile duct and causes severe pain.
While gallstones themselves are not usually fatal, their complications can be life-threatening if ignored. Untreated stones can lead to:
- Severe infection of the gallbladder (Gangrene).
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Gallbladder cancer (in cases of long-term chronic irritation).